JUMP TO
TRANSLATE
[google-translator]

OTHER VERSIONS OF THIS READING
INTRODUCTION
Freedom is a word we use often when we study American history, but it is an idea that we do not often stop to think much about. What is freedom? Is it freedom from something, such as control by a bad government, or is it freedom of something, such as the freedom to have your own religion without government telling you what to believe?
Maybe our idea of what freedom means in America has changed over time. For the first New England colonists, freedom was about religion, but today we want freedom from the fear of terrorism.
When the United States was started in the 1780s, the rich White men who got together in Philadelphian to create our current system of government had to decide what freedom meant to them and find a way to make sure people in the future would still be free. They knew that government had to protect, and not take away, freedom. Of course, their ideas about freedom and ours are different. Many of them owned slaves, which seems like the total opposite of our ideas about freedom.
What do you think? What is freedom?
DECLARING INDEPENDENCE
In the years before American independence, a new way of thinking called the Enlightenment became popular in Europe and America. Writers came up with new ideas about government, including questioning the right of kings to rule and suggesting that all humans were born with basic rights. Many of these ideas were written down in the Declaration of Independence as proof that America had the right to break away from England. Enlightenment ideas were also used to plan the American system of government.
Americans had been rebelling for many years against governments they thought were treating them unfairly. For example, in Pennsylvania, Virginia and North Carolina people had fought against their governments. Americans also had a long history of ignoring laws they did not like. Smuggling to avoid paying tariffs or to avoid mercantilist laws was normal. For many years, British leaders had not made the Americans follow trade laws since paying for the customs police cost more than the money they could get by making people pay the tariffs.
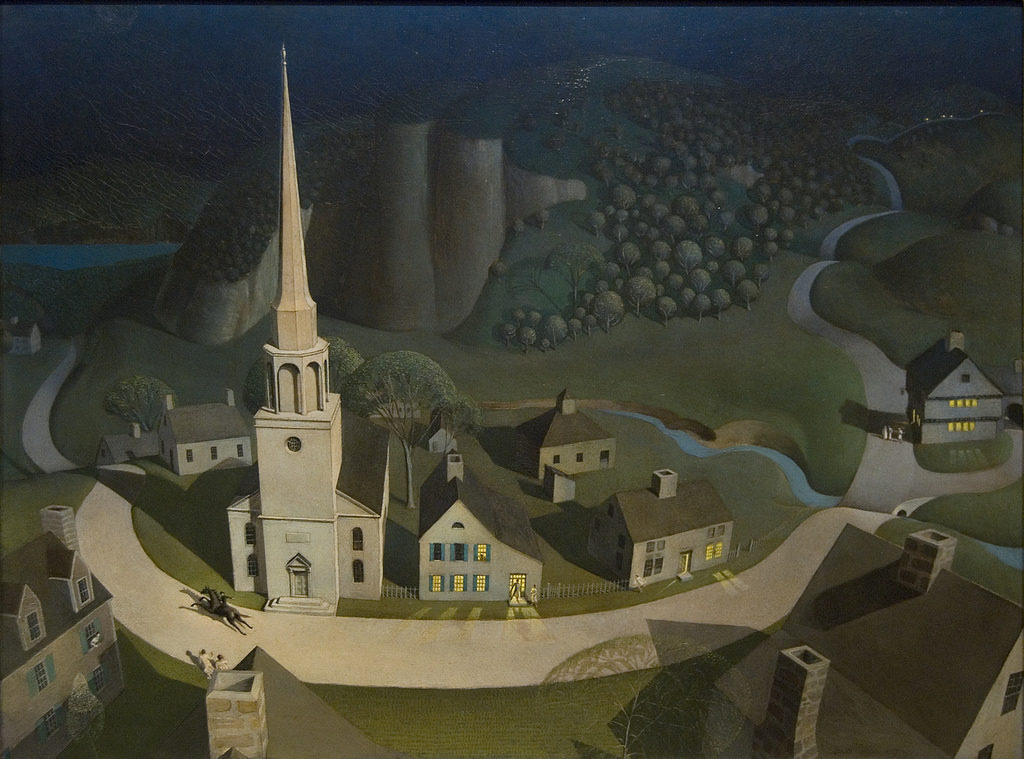
After the Seven Years War, the British government needed money and decided to start taxing the American colonists. This made Americans unhappy. When the British Parliament passed new laws to raise the taxes in America, the Americans protested. Most of all, Americans thought that it was not fair to tax them without letting them elect someone from America to go to England to vote in Parliament. They called this taxation without representation.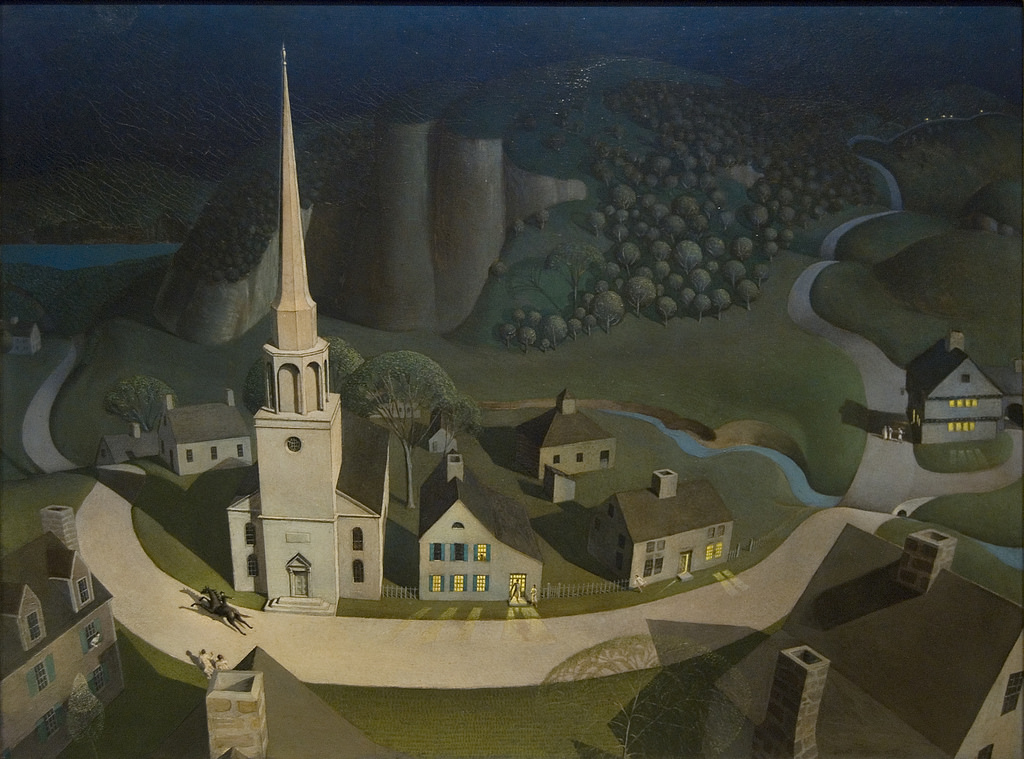 Secondary Source: Painting
Secondary Source: Painting
Grant Wood’s depiction of Paul Revere’s ride. Painted in 1931, Wood captures the drama of the event as seen from the perspective of many years later.
Grant Wood’s depiction of Paul Revere’s ride. Painted in 1931, Wood captures the drama of the event as seen from the perspective of many years later.
American patriots started groups like the Sons and Daughters of Liberty and Committees of Correspondence to plan protests, boycotts and to share ideas. They were an important first step in making a new national government by making plans and getting people to go along with boycotts and protests.
The Revolution started in Boston, Massachusetts. This is where the most famous protests happened, such as the Boston Massacre and Boston Tea Party. The British closed the port of Boston and Boston area patriots started militias to prepare for war. The fighting started when British soldiers tried to take guns the Americans had collected in the town of Concord a few miles from Boston.
The first battles of the American Revolution in April 1775 are called the Shot Heard Round the World because people in many other countries copied them and started their own revolutions, such as in Haiti and France.
When American leaders met in 1776 at the Second Continental Congress, fighting had already started in Boston. The American leaders voted to declare independence. They made a committee of five people to write a document explaining why they were going to separate from England. Ben Franklin, John Adams, and Thomas Jefferson were on the committee. Jefferson wrote most of the Declaration.
The Declaration of Independence tells some of the most important ideas about the meaning of the United States. In it, the Founding Fathers wrote that “all men are created equal.” They signed the Declaration on July 4, 1776, making it the country’s birthday.
The Declaration of Independence is one of the most important documents in American history. The introduction explains some basic ideas about freedom and the meaning of America. Over time we have changed our idea of what the Declaration means and who is included. For example, in the beginning the words “all men are created equal” only meant White men who owned land. Today, we include men and women of all races, rich, poor, and in between.
FIGHTING THE WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE
The British and Americans started the War for Independence with different strengths and weaknesses. The British were a strong country with the world’s biggest army and navy. The Americans knew the land and were fighting a war for a cause. The British had to win. The Americans just had to not lose and last long enough for the British to get tired and quit.
About 1/3 of Americans were patriots who wanted independence. About 1/3 were loyalists who wanted to stay a part of England. The last 1/3 didn’t care either way. After the war, many loyalists were treated badly, lost their land and moved to Canada.
Women helped in the war by making clothes and also helping the Continental Army as cooks and nurses, but most famously as spies. They also took over farms and businesses while their husbands were in the army.
The battles of the War for Independence were mostly victories for the British. In the early years of the war the Americans were able to fight back and get away, which gave the Americans hope and helped the soldiers stick with it thought the long war.
George Washington’s army spent the Winter of 1777 at Valley Forge where they learned how to fight and act like an army from rich Europeans who came to help the Americans.
The Americans could not have won without the help of France. At the end of the war, French ships blocked the British from getting out of Yorktown and Washington’s army forced the British to give up.
The Treaty of Paris of 1783 officially ended the war. Britain agreed that America was independent and gave the United States all the land south of Canada and west to the Mississippi River. Secondary Source: Painting
Secondary Source: Painting
This famous depiction of the Declaration of Independence is a 12-by-18-foot work by American John Trumbull. Trumbull painted many of the figures in the picture from life, and visited Independence Hall to depict the chamber where the Second Continental Congress met. It hangs in the rotunda of the United States Capitol Building in Washington, DC.
THE NEW GOVERNMENT
The new national government for the United States followed a set of rules called the Articles of Confederation. It gave most of the power to states and only some power to the national congress. This was because the Revolution had started because Americans didn’t like the powerful national government in Britain. Of course, this led to problems down the road.
Economic problems in the 1780s led to problems that showed why the new government wasn’t good enough. In Massachusetts, poor farmers didn’t have enough money to pay back loans and found themselves in danger of losing their land or going to debtor’s prison. Daniel Shays led a rebellion of these farmers against that state government. His rebellion failed, but it showed the divide between the rich who ran the government, and the rest of the people. It also showed the need for a federal, or national government to keep the peace.
Leaders met in Philadelphia to fix the problems with the Articles of Confederation. Their first important choice was to get rid of the Articles altogether and start over.
George Washington was the Constitutional Convention’s president, but James Madison was the one who really had clear ideas about how the new government could work, and he was the main author of the new Constitution.
One important choice the Founding Fathers had to make was about the legislature, or group of people who make the laws. States with a lot of people wanted a legislature that would have representation based on population. Smaller states liked a plan for equal representation for each state. The Great Compromise solved this problem and this is why our Congress today has a House of Representatives where states with more people have more representatives and a Senate where each state has two senators.
The Founding Fathers were worried about too much democracy. They created the Electoral College that would be a group of people to choose the president. This separated the president from the people, who they worried might not make a good decision. Our strange system of electing presidents today in a winner-take-all system is because of this early decision.
The Constitution did not get rid of slavery. In fact, it said that states had to help return runaway slaves and gave slave states extra power. Slaves could be counted as 3/5 of a person when states counted their people, so slave states got extra representatives in the House of Representatives.
The Constitution is not exciting to read. It is just a set of rules about how the government works. It tells things like the number of years the president serves, and what the things Congress can do. However, the introduction, or Preamble is famous. The Preamble tells the reasons we have a government. Its first words “We the People” also help us remember the idea that government is supposed to do what the people want and is chosen by the people.
PRESERVING THE RIGHTS OF INDIVIDUALS
The Constitution could not become law until 9 of the 13 states ratified, or voted for it. This led to an important time when people debated about the new plan for government. The main question was the balance of power between the states and the federal government. Also important was the idea of individual freedom and the power of government over people.
Federalists liked the new more powerful federal government. Alexander Hamilton and James Madison were Federalists. With John Jay they wrote the Federalists Papers to explain the reasons why the new Constitution was a good idea. Their work is still an important explanation of the ideas that the Founding Fathers had in mind when they made our system of government.
Anti-Federalists thought the new Constitution was dangerous. They thought that states should hold more power than the federal government. Thomas Jefferson led this group. Their most important problem with the Constitution was that there were no protections for regular people. The Federalists said that because power was separated between three branches of the government, no one in the government could become so powerful that they would be able to take away people’s rights, but in the end, the Anti-Federalists won the argument.
When the Constitution was adopted as the Federalists wanted, a Bill of Rights was added as the Anti-Federalists wanted. The Bill of Rights protects many of the basic freedoms that the British had violated before the Revolution. These include the right to free speech, press, religion, petition, and assembly. It says we have the right to a trial by jury, protection from warrantless search and seizure and the right to own a gun.
CONCLUSION
It has been said that freedom isn’t free, and the Patriots who won our freedom on the battlefields of the War for Independence are correctly remembered as American heroes. But what exactly is that freedom they fought to win?
The Founding Fathers first tried to protect our freedom through the Articles of Confederation, but farmers in Western Massachusetts fought against that government. In their minds, the rich people were using government to help themselves and taking away the freedom of the poor.
So, the Articles were thrown out and replaced by the Constitution which has guided us for the past 200 years. As the people in the states debated about ratifying the Constitution, they left documents that help us know what Americans thought freedom was at the time, and the Bill of Rights, the most important thing that came out of that debate, has helped us understand the idea of freedom even today. But what does freedom mean to you?
What is freedom?
CONTINUE READING

SUMMARY
BIG IDEA: Americans declared and fought for independence for a variety of reasons. Enlightenment ideas about government and economic factors were both important. These ideas were later incorporated into a new system of government.
The English settlers in America chose to declare and fight for independence after a long series of conflicts with their government. Most of these centered around economic problems and their right to participate in government. Americans were influenced by Enlightenment ideas.
American leaders did not want to declare independence right away and tried unsuccessfully to resolve their differences with the government in England. The Declaration of Independence laid out the reasons for independence and remains an important document in American history.
The War for Independence was long and difficult. Eventually with the help of the French, Washington’s army was able to force the British to surrender and recognize American independence.
For the first few years of American independence, the federal government was weak and ineffective at dealing with major problems. A rebellion in Massachusetts eventually pushed leaders to seek a new system of government.
The creation of the Constitution and our current system of government was due to problems that existed in the late 1780s and was the result of a series of compromises. The Founding Fathers tried to enshrine the ideals of the Revolution in a functioning system of government.
The debate about ratification of the new Constitution divided the nation’s leaders but led to the creation of the Bill of Rights.

VOCABULARY
![]()
PEOPLE AND GROUPS
Thomas Jefferson: Author of the Declaration of Independence and later third president.
George Washington: Virginia planter, surveyor, officer in the Seven Years War, leader of the Continental Army in the Revolution, President of the Constitutional Congress and First President of the United States.
James Madison: Father of the Constitution and later 5th President.
Founding Fathers: The American leaders who led the nation through the Revolution, establishment of the new government, and in the first years of the Constitution. They include George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, James Madison, Benjamin Franklin and Alexander Hamilton.
Federalists: One of the first two political parties. They supported the Constitution, strong central government, Hamilton’s financial plans, and favored Britain over France. Washington and Adams were the only president’s from this party.
Anti-Federalists: People opposed to the ratification of the Constitution. They feared tyrannical central government and successfully argued for the inclusion of the Bill of Rights. They later formed the Democratic-Republican Party.
![]()
KEY IDEAS
No Taxation Without Representation: Idea that the government should not levy taxes unless the people who must pay those taxes have the opportunity to elect members of that government.
Great Compromise: Compromised negotiated by James Madison at the Constitutional Convention resulting in a bicameral legislature with the Senate including two representatives from each state and the House with representation based on population.
![]()
DOCUMENTS
Declaration of Independence: Statement passed by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776 officially stating that the United States was independent from Britain.
Articles of Confederation: The plan for government created during the War for Independence. It featured a unicameral legislature, no executive, and favored state power over federal power. It proved ineffective and was replaced by the Constitution.
Constitution: The document that explains how the government works.
Bill of Rights: The first ten amendments to the Constitution. Ratified in 1791, they outline essential freedoms of all citizens.
![]()
EVENTS
First Thanksgiving: Celebration held in the fall of 1621 in Plymouth to celebrate the harvest. It was attended by both Pilgrims and their Native American friends.
Enlightenment: Time period in Europe and America in the 1700s characterized by an increased interest in science, new ideas about government and power, and a focus on order inspired by Classical Greece and Rome
Boston Massacre: Riot in 1770 between Boston citizens and British troops. It was exploited by Patriots to enflame anti-British sentiment.
Boston Tea Party: Protest by Boston Patriots led by Samuel Adams in which a cargo of tea was destroyed. It resulted in the closing of Boston Harbor.
Shot Heard ‘Round the World: Nickname for the opening battles of the American Revolution, so called because they inspired other Revolutionaries around the world.
July 4, 1776: The day the Declaration of Independence was signed. It is celebrated as America’s Independence Day.



